In a major leap towards building a sustainable future, researchers from Chalmers University of Technology have proposed a new concept for rechargeable batteries – made of cement. A report by SURFACES REPORTER (SR)
Researchers all across the world are baffled with the thought of providing a sustainable building material that could double up as clean energy source clubbed with cheaper cost and low maintenance. Now if a paper published by Doctor Emma Zhang, formerly of Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden and Professor Luping Tang is to be believed, the thought can be made possible with rechargeable cement-based battery.
The Concept
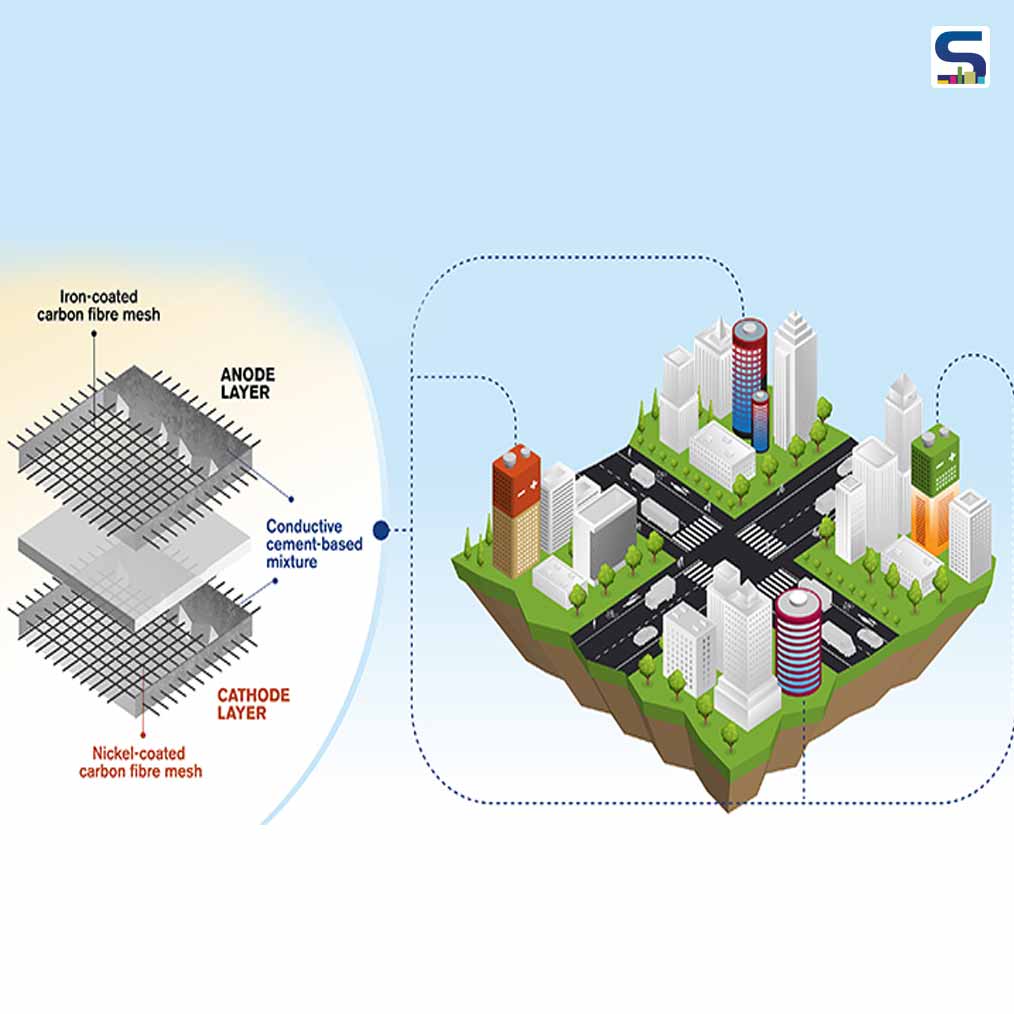
The concept involves first a cement-based mixture, with small amounts of short carbon fibres added to increase the conductivity and flexural toughness. Then, embedded within the mixture is a metal-coated carbon fibre mesh – iron for the anode, and nickel for the cathode. After much experimentation, this is the prototype which the researchers now present.
Read more: Auroville Design Consultants Used Eco-Friendly and Recycled Materials to Design Humanscapes Habitat in Tamil Nadu
“Results from earlier studies investigating concrete battery technology showed very low performance, so we realised we had to think out of the box, to come up with another way to produce the electrode. This particular idea that we have developed – which is also rechargeable – has never been explored before. Now we have proof of concept at lab scale,” Emma Zhang explains.
Luping Tang and Emma Zhang’s research has produced a rechargeable cement-based battery with an average energy density of 7 Watthours per square metre (or 0.8 Watthours per litre). Energy density is used to express the capacity of the battery, and a modest estimate is that the performance of the new Chalmers battery could be more than ten times that of earlier attempts at concrete batteries. The energy density is still low in comparison to commercial batteries, but this limitation could be overcome thanks to the huge volume at which the battery could be constructed when used in buildings.
A potential key to solving energy storage issues
The fact that the battery is rechargeable is its most important quality, and the possibilities for utilisation if the concept is further developed and commercialised are almost staggering. Energy storage is an obvious possibility, monitoring is another. The researchers see applications that could range from powering LEDs, providing 4G connections in remote areas, or cathodic protection against corrosion in concrete infrastructure.
Read more: This Low Cost, Fireproof, Bug-Proof, Eco-Friendly and DIY-Friendly Home is Made from Air Concrete |DomeGaia | Hajjar Gibran
“It could also be coupled with solar cell panels for example, to provide electricity and become the energy source for monitoring systems in highways or bridges, where sensors operated by a concrete battery could detect cracking or corrosion,” suggests Emma Zhang.
Read more: Casa COVIDA is a 3D Printed Home Made From Sand, Straw, Mud, Clay And Other Organic Materials | California | Emerging Objects
The concept of using structures and buildings in this way could be revolutionary, because it would offer an alternative solution to the energy crisis, by providing a large volume of energy storage. Concrete, which is formed by mixing cement with other ingredients, is the world’s most commonly used building material. From a sustainability perspective, it is far from ideal, but the potential to add functionality to it could offer a new dimension.
Emma Zhang comments, “We have a vision that in the future this technology could allow for whole sections of multi-storey buildings made of functional concrete. Considering that any concrete surface could have a layer of this electrode embedded, we are talking about enormous volumes of functional concrete”.
Challenges remain with service-life aspects
The idea is still at a very early stage. The technical questions remaining to be solved before commercialisation of the technique can be a reality include extending the service life of the battery, and the development of recycling techniques.
“Since concrete infrastructure is usually built to last fifty or even a hundred years, the batteries would need to be refined to match this, or to be easier to exchange and recycle when their service life is over. For now, this offers a major challenge from a technical point of view,” says Emma Zhang.
But the researchers are hopeful that their innovation has a lot to offer. “We are convinced this concept makes for a great contribution to allowing future building materials to have additional functions such as renewable energy sources,” concludes Luping Tang.
Text & Image source: Chalmers University of Technology
Keep reading SURFACES REPORTER for more such articles and stories.
Join us in SOCIAL MEDIA to stay updated
SR FACEBOOK | SR LINKEDIN | SR INSTAGRAM | SR YOUTUBE
Further, Subscribe to our magazine | Sign Up for the FREE Surfaces Reporter Magazine Newsletter
Also, check out Surfaces Reporter’s encouraging, exciting and educational WEBINARS here.
You may also like to read about:
Worlds Largest CO² capture & storage plant starts construction | Orca, Climeworks | Iceland | SR News
Carbon Fibre Entwined With Bamboo -The Material of the Future | Kengo Kuma
Know the Indian Architect who created Tiles from Polluted Air
And more…